This report summarizes Contrast Labs' analysis of real world application attack and vulnerability data from December 2019. By providing continuous insight and detection from inside applications, Contrast can identify and trend the way that attackers pursue applications and combine that with an understanding of if and when applications are vulnerable to those attacks.
This report builds on previous data that Contrast Security observed to highlight key trends and useful information in context. Developers, product owners, AppSec, and security engineers can use this information to better understand application security threats, adjust security controls, and improve their security posture.
By reading this report monthly and Contrast’s quarterly recap, AppSec teams can gain a better understanding of the possible types and origins of attacks and attackers.
Visit our website to learn more about how Contrast Security continuously measures both vulnerabilities and attacks in parallel across your application portfolio.
The chart below shows how the relative likelihood of vulnerabilities reported, as well as attacks by vector last month.
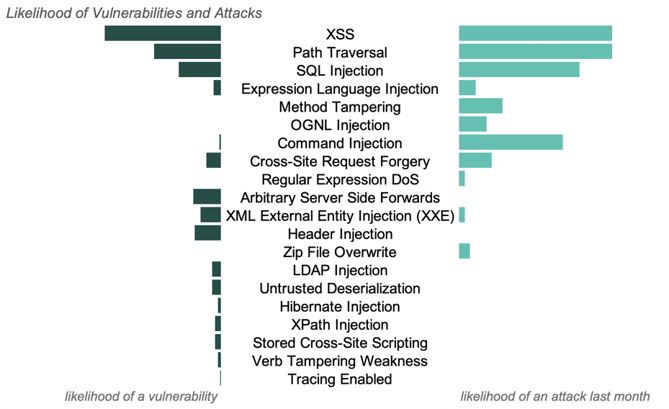
Over the course of the month, there were attack types detected with no likelihood of a vulnerability. In these instances, Contrast recorded an attack, such as an OGNL Injection attack, that never reached a corresponding vulnerability, i.e an OGNL Injection vulnerability, within the application’s code. These unsuccessful attacks are still reported, but de-prioritized by Contrast.
While these unsuccessful attacks can be statistically common, they have little impact on the security posture for a specific application. Instead, this information can be used to provide insight into what payloads attackers are using and understand the threat landscape at large.
CONTRAST WATCH LIST
A successful attack on a vulnerability can have wide-scale impact across many different organizations. It is critical for security teams to know about and properly manage library vulnerabilities, while also preparing for potential attacks.
Based upon the research included in this report, Contrast Labs shortlisted vulnerabilities that pose the highest risk to organizations. The list was created by combining the likelihood of a vulnerability and an attack (see previous chart) with the likelihood of a successful exploit and an impact factor. Below you can find this month's watch list.
Custom Code Vulnerabilities
Applications reported an average of 4 new, serious vulnerabilities in December. This is consistent with the number of vulnerabilities reported in November, but slightly down from the level seen in October.
The top 5 most prevalent serious vulnerabilities reported in custom code for the first time during December:
Vulnerabilities by Language
On average, Java and .NET applications reported the largest number of the following vulnerabilities:
Custom Code Vulnerabilities Targeted
Attacks on custom code made up over 99% of attacks last month. While libraries constitute the largest percentage of application source code, custom code makes up the largest source of vulnerabilities and attacks.
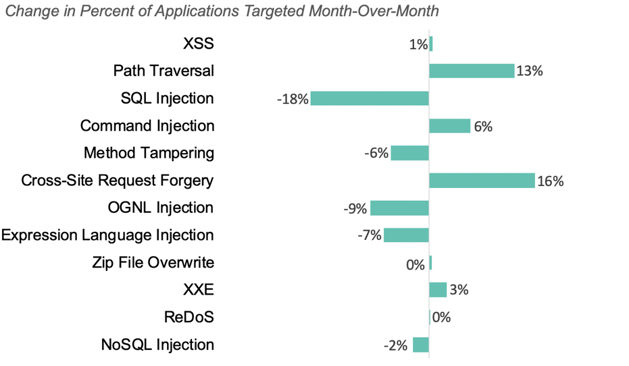
The three most common attack types in December were the same as November. We saw large increases in the number of applications targeted by all three types:
86% of applications were targeted by one of these three types during the month, down from 96% of applications in November.
The chart below shows how the percent of applications targeted changed for each attack type month-over-month, ordered in descending attack likelihood.
CVEs Targeted
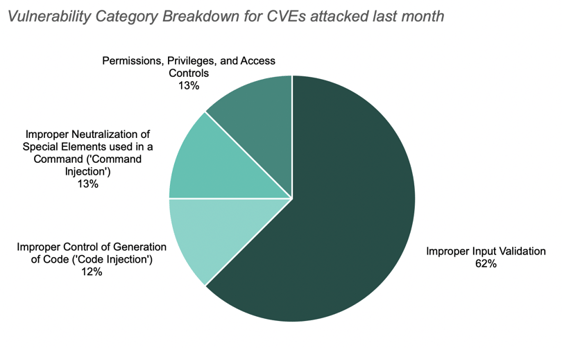
The top CVEs leveraged for attacks were CVE-2017-5638 (critical, improper input validation vulnerability), CVE-2014-0114 (unscored, improper input validation vulnerability), and CVE-2014-0112 (unscored, permissions, privileges, and access controls vulnerability).
The chart below shows the vulnerability category breakdown for CVEs attacked last month.
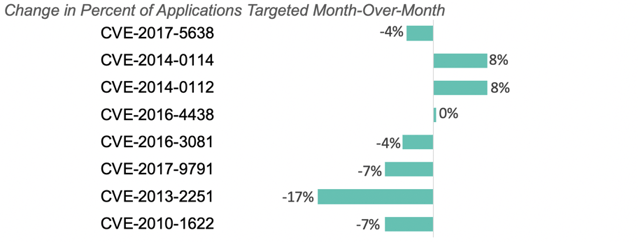
 There was a significant spike of applications with CVE-2014-0112 or CVE-2014-0114 targeted last month. Both of these CVEs resulted from a solution for CVE-2014-0094, a critical vulnerability that allows remote attackers to "manipulate" the ClassLoader via the class parameter.
There was a significant spike of applications with CVE-2014-0112 or CVE-2014-0114 targeted last month. Both of these CVEs resulted from a solution for CVE-2014-0094, a critical vulnerability that allows remote attackers to "manipulate" the ClassLoader via the class parameter.
The chart below shows how the percent of applications with CVEs attacked changed month-over-month, ordered in descending attack likelihood.
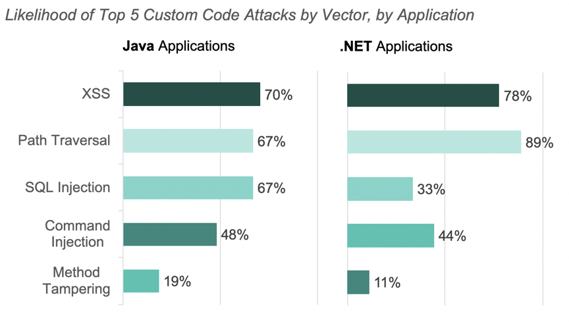
Attack Vectors by Language
Attacks targeting XSS, SQL Injection, Path Traversal, and Command injections vulnerabilities were the most prevalent attacks for Java and .Net applications in December.
The charts below show the percent of applications attacked, by vector, last month for both Java and .Net applications.
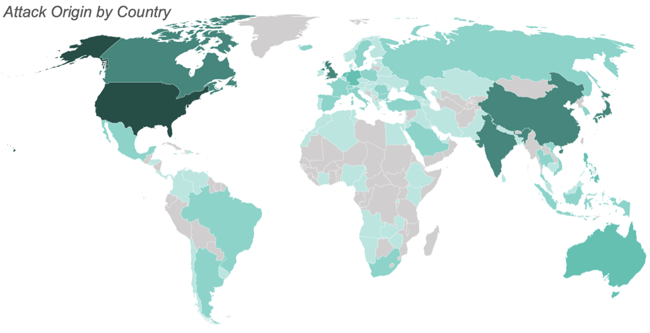
Attacks by Geolocation
December saw attacks from 108 countries. The greatest number of attacks originated from the United States, China, India, Japan, and Canada.
Japan moved up to the 4th most common origin country from 7th last month.
The map below illustrates the number of attacks originating from each country with the most saturated color representing the most attacks and the least saturated representing the least attacks. We observed no attacks from the countries filled in gray.
Get the latest content from Contrast directly to your mailbox. By subscribing, you will stay up to date with all the latest and greatest from Contrast.